 The result of all this is another link in the chain (we talked about this earlier). In the second example (from this article), it was a link in the flop chain.
The result of all this is another link in the chain (we talked about this earlier). In the second example (from this article), it was a link in the flop chain.
Second-level interpretation, i.e., interpreting real game situations, is a very complex matter. You will need to apply all the basic principles we discussed in other articles, which we will not discuss in this article.
The second example from the previous article clearly showed you how many things you need to consider even when interpreting a single statistic. As you have already seen, statistics from other betting rounds can help you interpret the current betting round.
The number of hands played in the interpretation chain
The statistic of the number of hands played is probably not unfamiliar to you. It indicates how many hands of the opponent you have in your poker database. This statistic also indicates the importance of other statistics for your interpretation, as all other statistics depend on the number of hands played. We introduced all these basic principles to you using the pyramid system in the first article on this topic about the importance of statistics in poker.
Configure your PokerTracker 4 HUD (VIDEO)
>>> Try PokerTracker 4 for free for 30 days <<<
Problems with statistics and the number of hands played
The number of hands played is too small: what now?
Before interpreting any statistics, you should first pay attention to the number of hands played. If the number of hands played is too small for a certain level, e.g., the turn, it is advisable to rely only on those statistics that require a smaller number of hands played. These are all first-level statistics, especially VPIP and PFR.
However, it is very important that you do not rely on other statistics that require a much larger number of hands played when making a decision. If you have only 50 hands, you should by no means rely on, for example, turn statistics (2nd barrel) or the opponent's pre-flop 3bet statistics. Although the number of hands played for these statistics is far too small, the programs still display these statistics, so be careful.
To avoid falling into these traps, get into the habit of first looking at the number of hands played before paying attention to other statistics.
If the number of hands played is too small to categorize your opponent into a certain player category, you should consider the opponent as an “unknown / unfamiliar opponent.”
Unknown player
Who is this “unknown player” you hear about so often? What are the main assumptions you can make about him?
 “Unknown players” strongly depend on the type of game and the dynamics of the limits. For example, an unknown player in NL10 is viewed completely differently than an unknown player in NL100. Let's assume that the unknown player has an average knowledge of poker for the limits he plays. The unknown player performs actions in each betting round that are typical for that limit. So, we assume that in passive limits, the playing style of players is more passive.
“Unknown players” strongly depend on the type of game and the dynamics of the limits. For example, an unknown player in NL10 is viewed completely differently than an unknown player in NL100. Let's assume that the unknown player has an average knowledge of poker for the limits he plays. The unknown player performs actions in each betting round that are typical for that limit. So, we assume that in passive limits, the playing style of players is more passive.
So, generally speaking, an unknown player is a player who plays like a typical regular player of those limits. You do not consider him an exceptional player and assume that he will play as is appropriate for those limits.
Missing statistics should be calculated from already known statistics – is it possible?
This situation becomes interesting when you do not see certain statistical values or when the number of hands played is too small for higher-level statistics (e.g., river statistics).
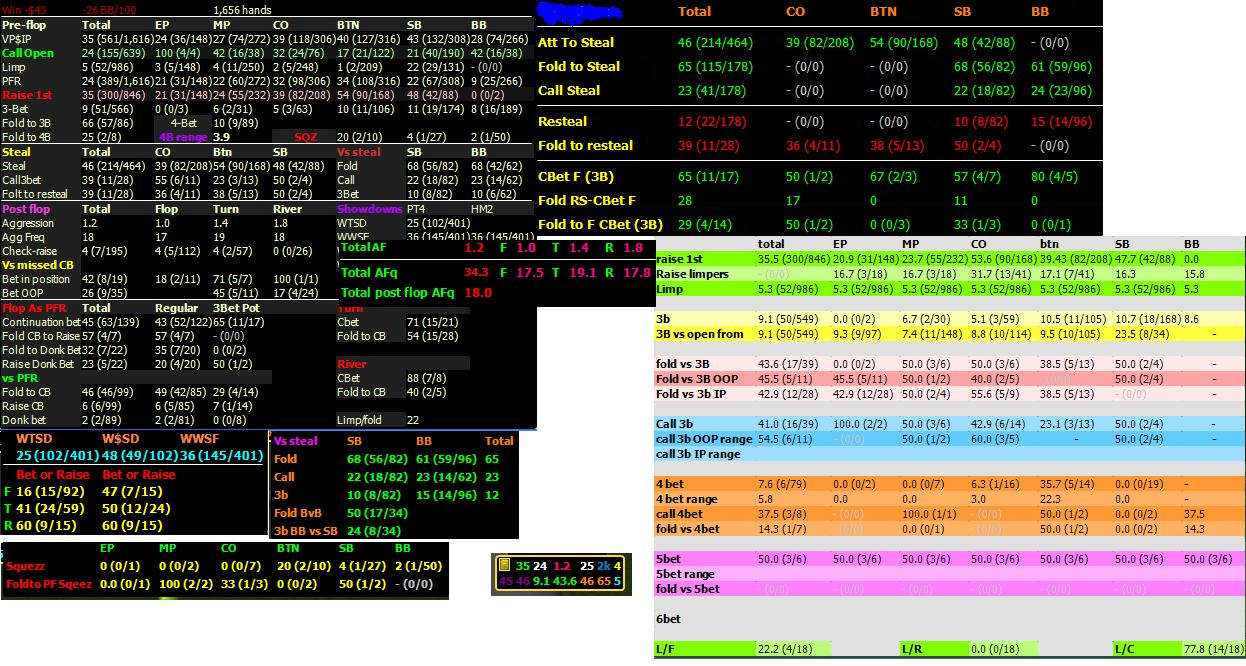
Suppose you are on the flop and have a sufficiently large number of hands played to make a second-level interpretation of the opponent. So, you have about 500 hands, but you want to accurately calculate the chances that the opponent, having made a bet on the flop, will make a bet on the turn (III – level statistics – 2nd barrel).
So, which statistics are important to us in this case? First of all, it is the opponent's flop range when he is the pre-flop aggressor (I PFR numerical value), his II continuation bet on the flop numerical value, and the opponent's AF and WTS statistics.
By interpreting these statistics, you can predict the likelihood that the opponent will make a continuation bet on the turn. Of course, when you are at the table, you also need to pay attention to the meta-game and other important factors, such as the cards on the table, position, number of opponents, etc. So, you need to pay attention to other important statistics and interpret them correctly.
So, as you can see, if you lack a certain statistic, you can calculate it yourself using other existing statistics. Interpreting statistics teaches you how to think properly by carefully analyzing the player's style and how to rely on certain statistics in the overall context. By interpreting statistics, you can determine the opponent's style and how you can apply the “missing statistic” to the opponent's playing style.
However, do not forget the main rule: the number of hands played is very important.
![]()
>>> Try PokerTracker 4 for free for 30 days <<<
The number of hands played is too large – can this be a problem?
You may often encounter this situation. Opponents, more or less successfully, develop their playing style depending on the limit. Therefore, regular players, whom you often see at the tables and whose number of hands played is particularly high, will adapt to the playing style over time and stop making certain mistakes that you could exploit.
After all, think about it – in your limits, you are also a regular player. So ask yourself – how much has your current game changed from the one you played a few months ago?
So it is logical that you should pay attention to the current number of hands played, because if the number of hands played is very large – the statistics are already several months old. During that time, the opponent's game could have changed significantly, but you will not notice this by looking at the statistics. But in any case, if you are in doubt – too many hands are always better than too few.
>>> Try PokerTracker 4 for free for 30 days <<<
Statistics and their trends
The main rule here is – the less specific a certain statistic is, the more stable its development will be. In this case, good examples are I VPIP and I PFR.
Statistics that depend on a certain situation tend to fluctuate more to one side or the other. For example, check-raise on the turn depends more on the current situation when you are trying to make a decision.
Can you judge an opponent based solely on statistics?
In this question, you should be able to answer without any problems. You already know that statistics are simply numbers indicating how often a certain action is performed. You also know that statistics must be interpreted on two levels, so just looking at statistics with the naked eye, they really mean nothing.
The first level is the interpretation of statistical averages in context. The second level is the interpretation of considerations from the first level in a gaming situation. At the second level, you need to pay attention to things like the cards on the table, hand history, table dynamics, reads, and other important factors that can influence the situation.
If you analyze your opponent's statistics well, over time you will understand that statistics describe the opponent's playing style much better than the cards they hold.
Each statistic is like a small piece from which we can assemble the whole picture that answers the question: “What is this player's playing style?” If you learn to interpret these small pieces correctly, you will be able to make many conclusions that will lead you to the right decisions at any time.
![]() Using PokerTracker filters and reports (VIDEO)
Using PokerTracker filters and reports (VIDEO)
Summary
After reading this article, you probably understand that even with all these poker programs and the information they provide about players, how you handle everything and process all the information you receive depends on you.
The numerical value of statistics must be interpreted correctly to make a profitable decision in the game. The numerical value of statistics is just a number that must be seen in the overall context. Interpretation chain nodes, which we have already discussed before, show how broadly a certain statistic can be used.
If you understand the content of this series of articles and understand all the dangers and pitfalls, soon you will be able to integrate a very powerful weapon into your game, which will help you win even more money.
Source: PokerGuru.lt
Where is the best place to play poker?